Computer System Architecture - Pipeline and Vector Processing
- Option : D
- Explanation : For 6 stages, non-pipelining takes 6 cycles
There were 2 stall cycles for pipelining for 25% of
the instructions
So pipe line time = [1+(2 25/100)] = 3/2 = 1.5
Speed up = Non– pipeline time/Pipeline time = 6/1.5
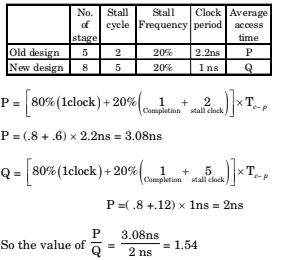
- Option : A
- Explanation : Speedup = Execution Time Old/Execution Time New Execution Time Old = CPI Old * Cycle TimeOld
[Here CPI is Cycles Per Instruction] = CPIOld * Cycle Time Old
= 4 * 1/2.5 Nanoseconds
= 1.6 ns
Since there are no stalls, CPUnew can be assumed 1 on average.
Execution Time New = CPInew
* Cycle Timenew
= 1 * 1/2
= 0.5
Speedup = 1.6/0.5 = 3.2