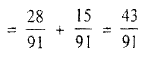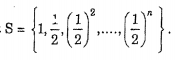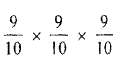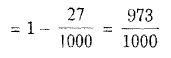Statistics - Probabilities
Let A and B be two events defined as
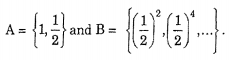
Then P (A ∩ B) will be
i.e., P(E1 ∪ E2 ∪ E3 .... ∪ En)
= P(E1) + P(E2) +.... + P(En)
This is
- Option : B
- Explanation : The five digits can be arranged in 5! ways, out
of which 4! will begin with zero.Total number of 5-figure numbers formed
= 5! - 4! = 96.
Those numbers formed will be divisible by 4
which will have two extreme right digits
divisible by 4,
i.e., numbers ending in 04, 12,20,24,32,40.
Now, numbers ending in 04 = 3! = 6,
numbers ending in 12 = 3! - 2! = 4,
numbers ending in 20 = 3! = 6,
numbers ending in 24 = 3! - 2! = 4,
numbers ending in 32 = 3! - 2! = 4,
and numbers ending in 40 = 3! = 6.
[Numbers having 12, 24, 32 in the extreme right
are (3! - 2!), since the numbers having zero on
t.he extreme left are to excluded.]
Total number of favourable ways
6 + 4 + 6 + 4 + 4 + 6 = 30
Hence, required probability =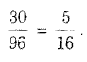
- Option : B
- Explanation : Two balls out 14 can be drawn in 14C2 ways which is the total number of outcomes.
Two white balls out of 8 can he drawn in 8C2 ways
Probability of drawing 2 white balls
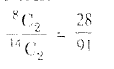
Similarly 2 red balls out of 6 call be drawn in
6C2 ways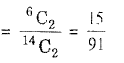
Probability of drawing 2 red balls
Probability of drawing 2 balls of the same
colour (either both white or both red)