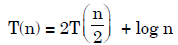Data Structures and Algorithms - Performance Analysis of Algorithms and Recurrences
- Option : A
- Explanation : Since f(n) = log n a = 2, b = 2 finding logba using master’s method = log22 = 1 Hence, f(n) = n' So, T(n) = Θ(n)
- Option : A
- Explanation : The time complexity is O (m + logn) So C = 1, d = 0, a = 0, b = 1 0 + 10 × 1 + 100 × 1 + 1000 × 0 = [110]
- Option : A
- Explanation : Unsorted array The algorithm perform find operation (log N)½ Insert operation N delete operation (log N)½ decrease key operations (log N)½ Hence unsorted array is best data structure for all above operations.
- Option : A
- Explanation : The subtrees are already Max-heap, so to make it half, we have to heap if the root, which takes Ω(log n) time.