Data Structures and Algorithms - Performance Analysis of Algorithms and Recurrences
- Option : D
- Explanation : The given function is recursive so the equivalent
recursion equation is
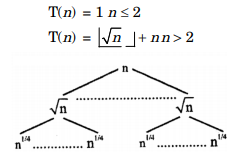 All the level sums are equal to n. The problem size at level k of the recursion tree is n2– k and we stop recursing when this value is a constant.
Setting n2–k = 2 and solving for k gives us
2– klog2n = 1
2k = log2n
k = log2 log2n
So T(n) = θ(log2 log2n)
All the level sums are equal to n. The problem size at level k of the recursion tree is n2– k and we stop recursing when this value is a constant.
Setting n2–k = 2 and solving for k gives us
2– klog2n = 1
2k = log2n
k = log2 log2n
So T(n) = θ(log2 log2n)
- Option : B
- Explanation : Since, 2n – c = average number of comparison needed. 1.5 n – 2 = number of comparison in case. n log2n = also doesn't conform with number of comparison needed.
- Option : A
- Explanation : B & E are exponential functional so {B, E} > {A, C, D} * for larger value of n E > B. * A < C (clearly power is less) * D < C for larger value of n So A < D < C < E < B.
- Option : A
- Explanation : Given if n = 1 then T (1) = 1 So put n = 1 in all options only option (A) gives 1


