UGC NET Management Previous Year Solved Papers - November 2017
- Option : C
- Explanation : Objectives of Financial Management Financial management of any business firm has to set goals for itself and to interpret them in relation to the objective of the firm. Broadly, there are two alternative objectives a business firm can pursue viz.
> Profit Maximisation: Profit maximization is considered as an important goal in financial decision-making in an organization. It ensures that firm utilizes its available resources most efficiently under conditions of competitive markets. But in recent years, under the changed corporate environment, profit maximisa-tion is regarded as unrealistic, difficult, unappropriate and socially not much preferred goal for business organisation. Profit maximisation as corporate goal is criticised by scholars mainly on the following grounds:
(i) It is vague conceptually.
(ii) It ignores timing of returns.
(iii) It ignores the risk factor.
(iv) It may tempt to make such decision which may in the long run prove disastrous.
(v) Its emphasis is generally on short run projects.
(vi) It may cause decreasing share prices.
(vii) The profit is only one of the many objectives and variables that a firm considers.
> Wealth Maximisation: Presently, maximisation of present value (or wealth) of a course of action is considered appropriate operationally flexible goal for financial decision-making in an organisation. The net present value or wealth can be defined more explicitly in the following way.
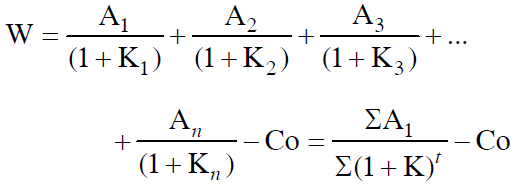
Where A1.... A2 represent the stream of benefits expected to occur if a course of action is adopted. Co is the cost of that action and K is the appropriate discount rate, and W is the Net present worth or wealth which is the difference between the present worth or wealth of the stream of benefits and the initial cost.
The management of an organisation maximises the present value not only for shareholders but for all including employees, customers, suppliers and community at large. This goal for the maximum present value is generally justified on the following grounds:
(i) It is consistent with the object of maximising owners economic welfare.
(ii) If focuses on the long run picture.
Goal Objective Advantages Disadvantages Profit Maximisation Large amount of profits 1. Easy to calculate profits 1. Emphasizes the short term 2. Easy to determine the link between financial decisions and profits 2. Ignores risk or uncertainty 3. Ignores the timing of returns 4. Requires immediate resources Shareholder wealth maximisation Highest market value of common stock 1. Emphasizes the long term 1. Offers no clear relationship between financial decisions and stock price 2. Recognizes risk or uncertainty 2. Can lead to management anxiety and frustration 3. Recognizes the timing of returns 4. Considers return
19. Beta (β) is a measure of :
- Option : A
- Explanation : Beta (β): One of the most popular statistical methods is standard deviation or variance used to measure the total risk (Systematic Risk + Unsystematic Risk) associated with a security. The systematic risk of a security can be measured by a statistical measure known as beta (β). In other words, the measure of quantifying the systematic risk of a stock is referred to as beta (β) analysis or volatility. Accordingly, the beta factor is the measure of the volatility of the systematic risk of a security or investment in the portfolio. It measures how the price of stock responds to market movements. It shows the extent to which the systematic risk of a security is correlated with the variability of the overall stock market.
The beta factor explains the correlation coefficient between the returns on a market portfolio of investments and the returns on a particular stock or investment.
Beta of a security is calculated by using historical data of returns of the security as well as a representative stock market index. The beta factor of the market as a whole is 1.0. The degree of volatility of the systematic risk of an asset may be expressed as either positive (above-average risk), negative, or zero (below-average risk).
20. Capital budgeting is concerned with :
- Option : D
- Explanation : Capital budgeting is the process by which corporations decide what investments to make in long-term real capital assets and investment projects and how to finance those investments with the proceeds from newly issued or existing financial capital claims. Most firms undertake a serious capital budgeting exercise at least annually. When a firm’s funds are limited and its capital budget constrained by an unwillingness or inability to issue new securities, the capital budgeting process is also sometimes called capital rationing or capital allocation.


