PREVIOUS YEAR SOLVED PAPERS - June 2019
- Option : A
- Explanation : Securities premium, similar to share capital, can’t be returned to the shareholders. However, Section 52 of the Companies Act, 2013 provides that the balance in the securities premium account can be utilized for the following purposes:
1. Issuing fully paid bonus shares.
2. Writing off the preliminary expenses of the company.
3. Writing off the expenses of, or commission paid or discount allowed on, an issue of shares or debenture of the company.
4. Providing for the premium payable on the redemption of redeembale preference shares or debentures of the company.
- Option : A
- Explanation : The relationship between price, elasticity and marginal revenue is given as follows:
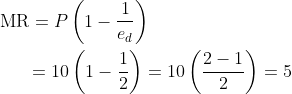
15. Which of the following is an instance of non-conventional dumping?
- Option : C
- Explanation : Dumping is a form of price discrimination. Under dumping the international company charges different prices for the same product in different markets. Dumping means selling the products at below the cost of production or at below the on going price in the market. Consequently, the imported goods are sold at prices so low as to be detrimental to local producers of the same kind of merchandise.
Types of Dumping
∎ Sporadic dumping: Sporadic dumping occurs when an international company sells its unsold inventories in a foreign country to get rid of them.
∎ Predatory dumping: Predatory dumping is selling the product in a foreign market at a loss as a strategy of entering the market. Zenith uses this strategy for selling televisions and computers.
∎ Persistent dumping: Persistent dumping involves consistently selling the product at lower prices in one market than in other markets. Japan sells its electronic products at high prices in Japan and sells the same products consistently at lower prices in the USA and India.
∎ Reverse dumping: Under reverse dumping the product is sold at a high price in international markets and at a low price in the domestic market.


