PREVIOUS YEAR SOLVED PAPERS - December 2018
- Option : B
- Explanation : Three of the strategies for entry into foreign markets — contracts, joint ventures and direct foreign investments — present greater challenges when faced with different goals: social welfare for the developing country and profits for the firm. These market entry strategies may affect multiple market participants and provide the opportunity for a differing risk/reward ratio. The profit potential of each entry mode depends on characteristics of the market to which the strategy is applied.
- Option : D
- Explanation : Cost-Plus Pricing: With cost-plus pricing, the seller’s costs are determined (usually during a project or after a project is completed), and then a specified dollar, amount or percentage of the cost is added to the seller’s cost to establish the price. Costplus pricing and competition-based pricing are in fact the most common bases for pricing services. When production cost are difficult to predict, cost-plus pricing is appropriate. Projects involving custom-made equipment and commercial construction are often priced using this technique. The government frequently uses such cost-based pricing in granting defense contracts. One pitfall for the buyer is that the seller may increase costs to establish a larger profit base. Furthermore, some costs, such as overhead, may be difficult to determine. In periods of rapid inflation, cost-plus pricing is popular, especially when the producer must use raw materials that are fluctuating in price. In industries in which cost-plus pricing is common and sellers have similar costs, price competition may not be especially intense.
- Option : C
- Explanation : The regression coefficients byx and bxy may be expressed in terms of the correlation coefficient (r) and the standard deviations of x and y (viz. σx and σy) by the relations
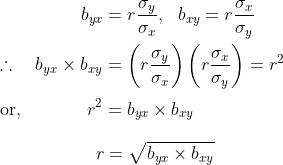
Thus, the correlation coefficient r is the geometric mean of the two regression coefficients byx and bxy.
- Option : B
- Explanation : Predictability and Stability: Predictability and stability are important objectives of the multilateral regulation of trade. The multilateral trading system is an attempt by governments to make the business environment stable and predictable as sometimes, promissing not to raise a trade barrier can be as important as lowering one, because the promise gives businesses a clearer view of their future opportunities. With stability and predictablility, investment is encouraged, employment opportunities are generated and consumers can fully enjoy the benefits of competition.


