PREVIOUS YEAR SOLVED PAPERS - GATE 2020
- Option : B
- Explanation : Statement I - L = {an| n ≥ 0} ∪ { anbn | n ≥ 0} ↓ ↓ Linear power well know DCFL ∴ it is regular ∴ L = Regular ∪ DCFL {use the closure properties} L = DCLF Statement--III As we cannot write LL( k ) grammar, for any value of k, Hence statement III is correct.
- Option : B
- Explanation : Statement I – False, symbol table can be accessed during any phase of compiler. Statement II- False, For recursion support it is not necessarily be heap storage, as stack storage also supports recursion. Statement III – False, “Variable must be declared before use” are detected during semantic analysis. Hence, None of the statements is correct.
- Option : A
- Explanation : Given steps:
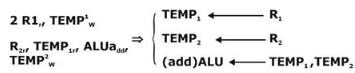
1. R2r, TEMP1r, ALUadd, TEMP2W
2. R1r, TEMP1W
3. PCr, MARW, MEMr
4. TEMP2r, ROW
5. MDRr. IRW
Instruction fetch is first step to be done which is indicated by step 3 and 5
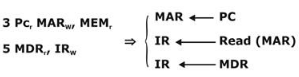 Then instruction decoded by cu and then operand fetch should be performe
D. If is indicated with step 2 and operand fetch and perform operation by step 1
Then instruction decoded by cu and then operand fetch should be performe
D. If is indicated with step 2 and operand fetch and perform operation by step 1
 4. Now, write result operations should be performe
D. It is indicated by step 4, as a result, should be in R0.
Step4:
4. Now, write result operations should be performe
D. It is indicated by step 4, as a result, should be in R0.
Step4:
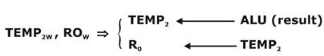 Hence correct order of execution should be, 3, 5, 2, 1, 4
Hence correct order of execution should be, 3, 5, 2, 1, 4


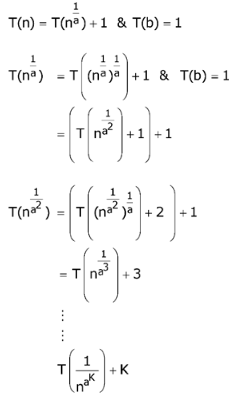 ⇒ loga logbn
⇒ O(loga logbn)
⇒ loga logbn
⇒ O(loga logbn)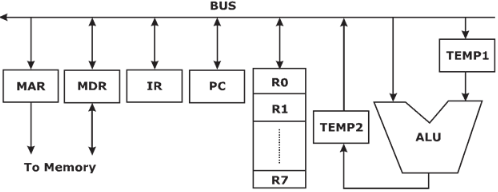
 1,2,4 are True
1,2,4 are True