UGC NET COMMERCE July 2018 Q25
0. For a standard normal probability distribution, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ) are:
- Option : A
- Explanation : Standard Normal Probability Distribution: To deal with problems where the normal probability distribution is applicable, the value of random variable x is standardized by expressing it as the number of standard deviations (σ) lying on both sides of its mean (μ). Such standardized normal random variable, z (also called z-statistic, z-score or normal variable) is defined as:
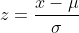
or equivalently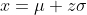
The z-statistic measures the number of standard deviations that any value of the random variable x falls from the mean. From formula, we may conclude that
(i) When x is less than the mean (μ), the value of z is negative.
(ii) When x is more than the mean (μ), the value of z is positive.
(iii) When x = μ, the value of z = 0.
Standard Normal Probability Distribution:
A normal probability distribution with mean equal to zero and standard deviation equal to one.


