PREVIOUS YEAR SOLVED PAPERS - GATE 2017 Shift 1
- Option : B
- Explanation :
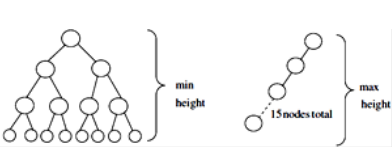 Min height = floor(log2N) = floor(log215)=3
Max height n-1 = 14, when the tree is either left skewed or right skewed.
Min height = floor(log2N) = floor(log215)=3
Max height n-1 = 14, when the tree is either left skewed or right skewed.
- A
Q0Q1 after the 3rd cycle are 11 and after the 4th cycle are 00 respectively


- B
Q0Q1 after the 3rd cycle are 11 and after the 4th cycle are 01 respectively


- C
Q0Q1 after the 3rd cycle are 00 and after the 4th cycle are 11 respectively


- D
Q0Q1 after the 3rd cycle are 01 and after the 4th cycle are 01 respectively


- Option : B
- Explanation :
After 3rd clock pulse :11 After 4th clock pulse: 01 Qt can be observed from the diagram that : Q0 Q1 after the 3rd cycle are 11 and after the 4th cycle are 01 Therefore, option B is correctCLK Q1 Q0 0 1 1 1 0 1 2 1 0 3 1 1 4 0 1
- Option : C
- Explanation : In given function foo every time in the while foo is called value 3 because val is passed with post decrement operator so the value 3 is passed and val is decremented later. Every time the function is called a new variable is created as the passed variable is passed by value, with the value 3. So the function will close abruptly without returning any value. In the function bar, in the while loop value the value of val variable is not decrementing, it remains 3 only. Bar function in the while loop is called with val-1 i.e 2 but value of val is not decremented, so it will result in infinite loop.
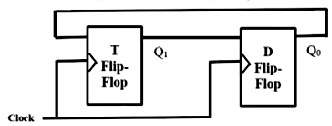 Initially, both Q0 and Q1 are set to 1 (before the 1 clock cycle). The outputs
Initially, both Q0 and Q1 are set to 1 (before the 1 clock cycle). The outputs