Computer Networks - Computer Networks Section 3
- Option : D
- Explanation : Consider optimum packet size which required
minimum number of packet and does not waste
any space.
Here consider each packet header because they are all work on packet switching network. 3 bytes is header size;
9 – 3 = 6 is data size
24/6 = 4 are the required packet
For case 1 : 24 packets are required
For case 2 : 8 packets are required
For case 3 : 6 packets are required
- Option : A
- Explanation : Goodput (is the application level throughput) = Successfully delivered data/ Time = (i-N)/i = 1- N/i.
- Option : A
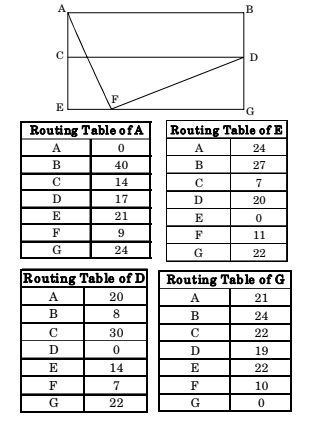
- Explanation : Distance from F to F is 0 So option C is false.
Using Distance Vector routing protocol, F → D →
B distance is 20
So option B and D is also false.
- Option : C
- Explanation : As per question, we have to count average hops
per message.
Steps used:
1) Message goes up from sender to root.
2) Message comes down from root to destination
1) Average hops message goes to root – ((3 * 8) + (2 * 4) + (1 * 2) + (0 * 1))/15 = 2.267 // 3 * 8 means represents 3 hops & 8 routers for Bottom most level & So on.
2) Similarly average hops when message comes down -
((3 * 8) + (2 * 4) + (1 * 2) + (0 * 1))/15 = 2.267
So, Total Hops = 2.267 + 2.267 = 4.53.