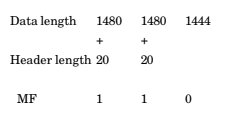Computer Networks - Computer Networks Section 3
- Option : A
- Explanation :
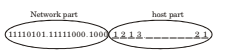
Since half of 4096 host addresses must be given to organization A, we can set 12th bit to 1 and include that bit into network part of organization A, so the valid allocation of addresses to A is 245.248.136.0/21
Now for organization B, 12th bit is set to ‘0' but since we need only half of 2048 addresses, 13th bit can be set t o ‘0' and include that bit into network part of organization B so the valid allocation of addresses to B is 245.248.128.0/2.
- Option : C
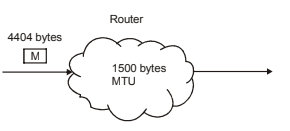
- Explanation : Since M bit is 0, so there is no fragments after
this fragment. Hence this fragment is the “last
fragment” Tow, H LEN defines t he length of
Header in datagram. Since H LEN is 10 so size of
header is 10 * 4 = 40B.
Length of data = Total length – Leader length = 400 – 40 = 360 B.
Few, fragment offset of data in original datagram is measured in units of 8B. So to find first Byte of this fragment,
first Byte/B = fragment offset
first Byte = 300 * 8 = “2400” B
since length of data is 360B
so last Byte on this datagram will be “2759” B

30. Consider the following routing table at an IP
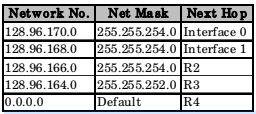
For each IP address in Group-I identify the correct choice of the next hop from Group-II using the entries from the routing table above.
| List-I | List-II |
| A. 128.96.171.92 | 1. Interface 0 |
| B. 128.96.167.151 | 2. Interface 1 |
| C. 128.96.163.121 | 3. R2 |
| D. 128.96.165.121 | 4. R3 |
| 5. R4 |
Codes:
| A | B | C | D | |
| (I) | 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| (II) | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 |
| (III) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| (IV) | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 |